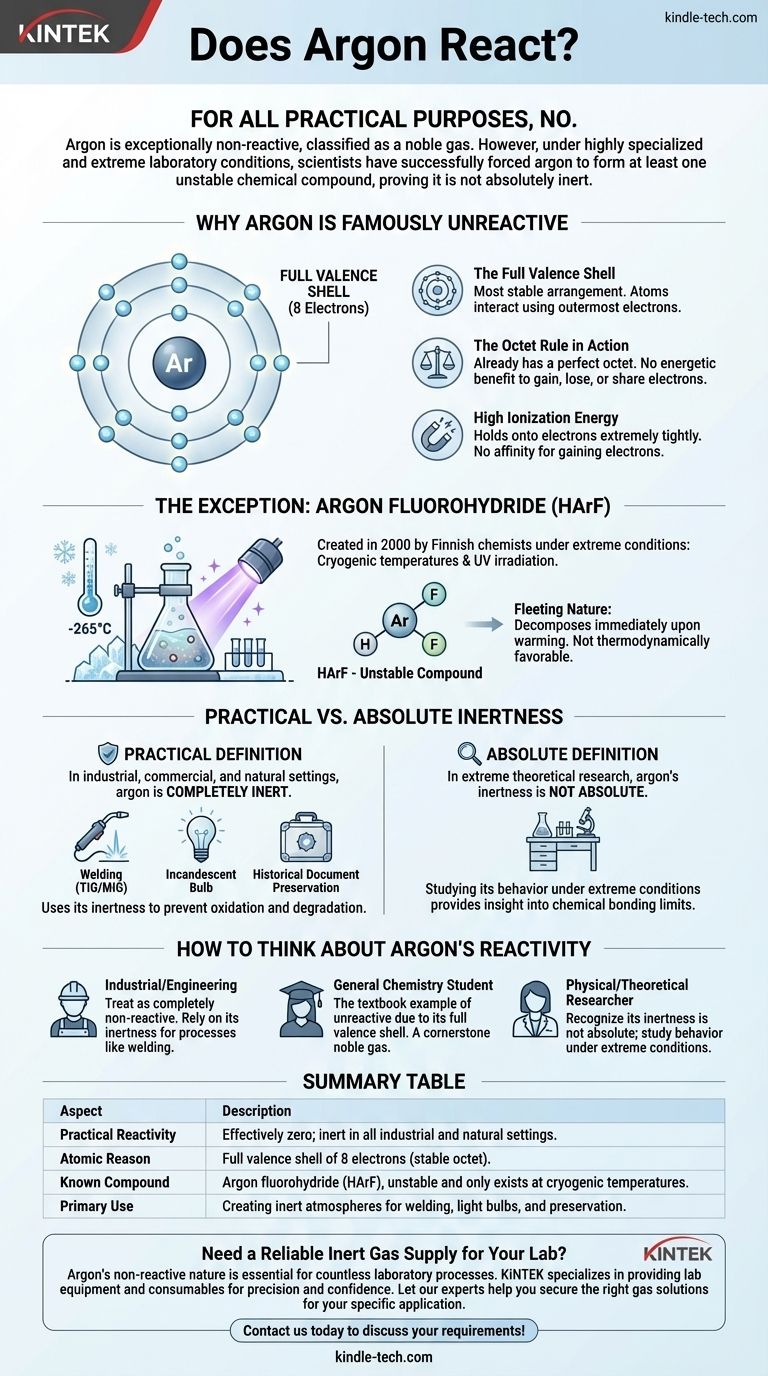
从所有实际目的来看,不会。氩气具有极强的非反应性,这就是它被归类为惰性气体的原因。然而,在高度专业化和极端的实验室条件下,科学家们已经成功地迫使氩气形成至少一种不稳定的化合物,证明它并非绝对惰性。
核心要点是,元素的“反应性”并非一个简单的“是”或“否”问题。虽然氩气完美的电子壳层结构使其在任何自然或工业环境中都是惰性的,但其非反应性可以在低温条件下通过足够的能量克服,揭示了化学键合的微妙复杂性。
为什么氩气以“不活泼”而闻名
要理解为什么氩气如此强烈地抵抗形成化学键,我们必须审视其原子结构。它惰性的名声并非随意得来;它是其电子构型的直接结果。
完整的价电子层
原子通过其最外层的电子(称为价电子)进行相互作用并形成键。
氩气有八个价电子,这完全填满了它的外层电子壳层。这是原子所能拥有的最稳定的排列。
“八隅体规则”的作用
“八隅体规则”是化学中的一个基本原理,指出原子倾向于获得、失去或共享电子以达到八个电子的完整外层壳层。
因为氩气已经拥有这个完美的八隅体,所以它没有能量上的好处去获得、失去或与其他原子共享电子。它已经处于其理想的低能量状态。
高电离能
电离能是使电子从原子中脱离所需的能量。氩气具有非常高的电离能,这意味着它非常紧密地 удерживает 它的电子。
同样,它对获得电子也没有亲和力。在正常情况下,氩气根本没有化学上的“动机”参与反应。

证明规则的例外
几十年来,氩气一直被认为是完全惰性的。这种情况在2000年发生了改变,当时一个芬兰化学家团队首次创造了已知的真正氩化合物。
在极端条件下强制反应
这种化合物,氟氢化氩(HArF),并非在普通的实验室烧杯中制备。
科学家们必须将氩气和氟化氢的混合物冷冻到接近绝对零度(约-265°C或-445°F)的表面上,然后用强大的紫外线照射。这种极端的能量输入足以暂时迫使不情愿的氩原子形成键。
氩化合物的短暂性
生成的HArF化合物极其不稳定。它只存在于这些低温下。
如果稍微加热,弱键就会断裂,它会立即分解回单独的氩气和氟化氢。这突出表明该化合物在热力学上是不利的,并且仅因为被极端低温“困住”而存在。
实际惰性与绝对惰性
这一发现迫使我们区分两个概念:实际意义上的真实和绝对理论意义上的真实。
惰性的实际定义
在任何工业、商业或自然环境中,氩气都是完全惰性的。它不与空气、水、金属或任何其他接触到的物质发生反应。
正是这种实际的惰性使其如此有价值。
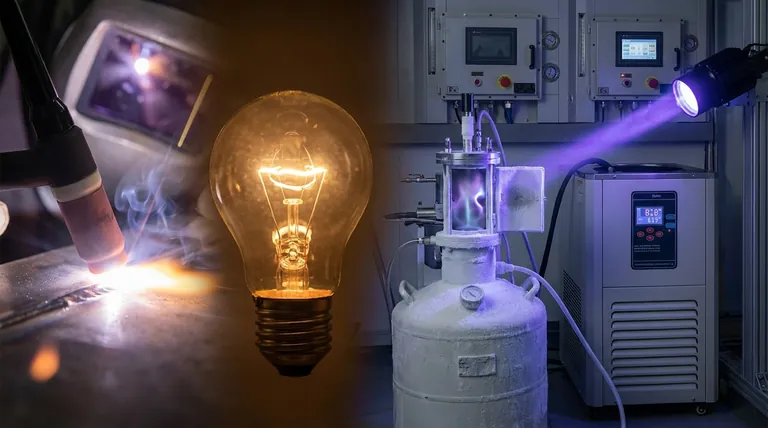
为什么这对于应用很重要
氩气的非反应性是一个特点,而非局限。在焊接(TIG/MIG)中,它在熔融金属周围形成一个惰性“保护层”,防止其氧化或与空气中的气体发生反应,从而确保焊接清洁、牢固。
在白炽灯泡中,氩气气氛可以防止炽热的钨丝烧断。在历史文献保存中,它提供了一个无氧环境以阻止降解。
如何看待氩气的反应性
您的具体情境决定了您应该如何看待氩气的化学行为。理解这种区别是正确应用化学原理的关键。
- 如果您在工业或工程环境中工作:将氩气视为一种完全非反应性气体。它的惰性是其最有价值的特性,可以信赖它用于焊接和制造等过程。
- 如果您是普通化学专业的学生:了解氩气是惰性元素的典型例子,因为它具有完整的价电子层,使其成为惰性气体组的基石。
- 如果您是物理或理论化学研究人员:认识到氩气的惰性并非绝对,研究其在极端条件下的行为为化学键合的极限提供了宝贵的见解。
最终,氩气极度不愿反应是其基本特性,使其在科学上既有趣又在现实世界中极其有用。
总结表:
| 方面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 实际反应性 | 实际上为零;在所有工业和自然环境中均呈惰性。 |
| 原子原因 | 完整的8个价电子层(稳定的八隅体)。 |
| 已知化合物 | 氟氢化氩(HArF),不稳定,仅存在于低温下。 |
| 主要用途 | 为焊接、灯泡和保存创造惰性气氛。 |
需要可靠的实验室惰性气体供应?
氩气的非反应性对于无数实验室过程至关重要,从创建受控气氛到敏感材料处理。确保您拥有持续、高纯度的供应对于您的实验结果至关重要。
KINTEK 专注于提供您精确和自信操作所需的实验室设备和耗材。让我们的专家帮助您为您的特定应用获得合适的燃气解决方案。
立即通过我们的表格联系我们,讨论您的需求!
图解指南