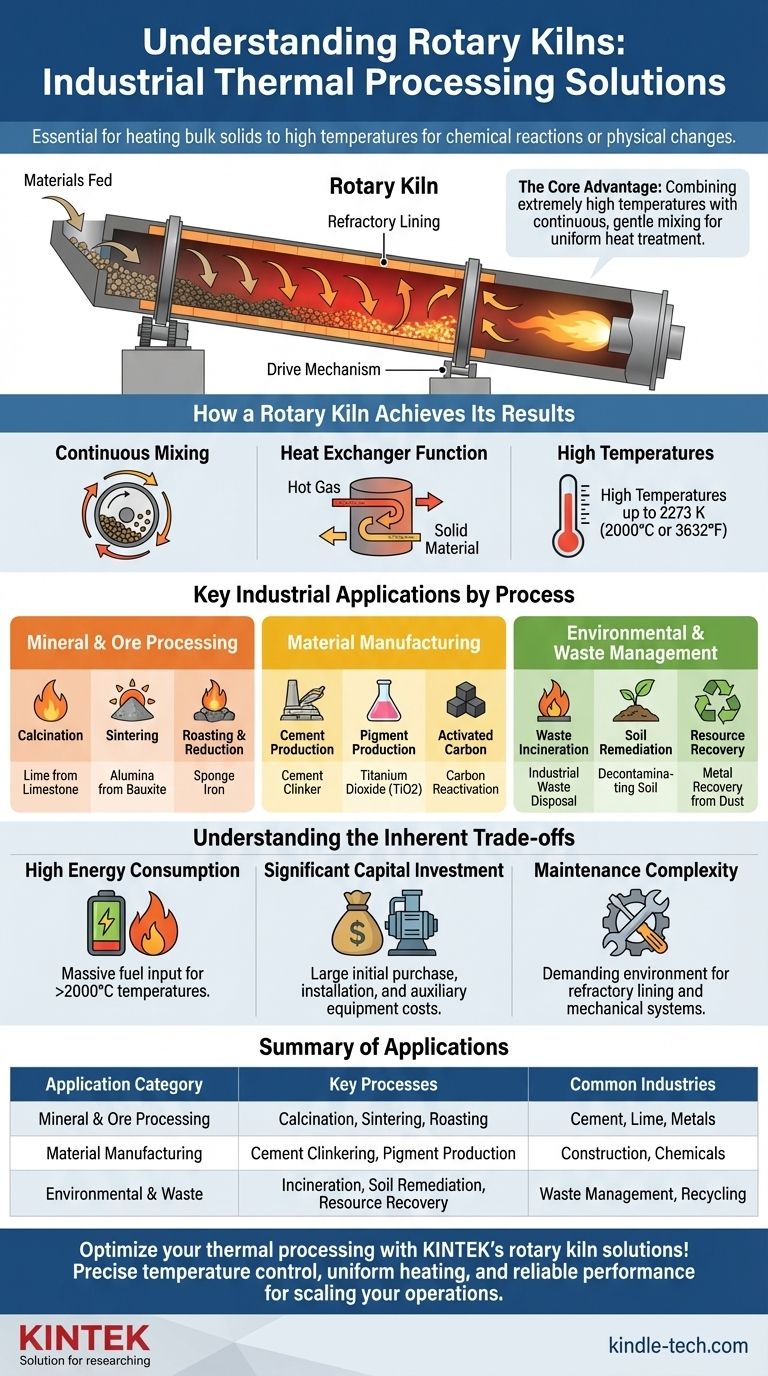
从核心来看,回转窑是用于热处理固体材料的工业炉。在任何需要将散装固体加热到极高温度以引起化学反应或物理变化的工艺中,它们都至关重要。其应用范围从生产水泥和石灰等基本商品,到先进材料制造和环境修复,例如焚烧废物或净化土壤。
回转窑的真正价值在于它能够将极高的温度与连续、温和的混合相结合。这种独特的组合确保了均匀的热处理,使其成为在工业规模上引起固体材料物理和化学变化的理想环境。
回转窑如何实现其效果
回转窑的有效性源于其简单而强大的设计:一个长而旋转的圆筒,内衬耐火材料,略微倾斜以允许重力使材料通过。
连续混合原理
随着窑体缓慢旋转,内部的固体材料不断被提升和翻滚。这种连续的搅拌,或称级联运动,确保每个颗粒都暴露在流经圆筒的热气中。
这个过程保证了颗粒床的充分混合,这对于实现均匀的温度分布和一致的产品质量至关重要。
作为热交换器的功能
从根本上说,回转窑充当着一个高效的逆流热交换器。由下端燃烧器产生的热气体沿窑体向上流动,与向下移动的固体材料流向相反。
这种设计最大限度地将热能从热气相传递到固体材料,使其在通过窑体长度时发生必要的转变。
高温的力量
回转窑经过精心设计,能够达到令人难以置信的高温,通常高达 2273 K(2000°C 或 3632°F)。这种能力对于化学还原和矿物相变等能源密集型工艺至关重要,这些工艺在较低温度下是不可能实现的。

按工艺划分的关键工业应用
回转窑的多功能性意味着它被应用于数十个行业。这些应用可以分为几个主要类别。
矿物和矿石加工
这是最常见的用途,其中原材料被转化为更有价值的产品。
- 煅烧:通过加热分解材料,例如从石灰石生产石灰或从铝土矿生产氧化铝。
- 烧结:使固体颗粒在不熔化的情况下熔合在一起,用于白云石和菱镁矿等材料。
- 焙烧和还原:化学改变矿石,例如还原铁矿石以生产海绵铁或焙烧钛铁矿。
材料制造
回转窑是许多基本工业和化学产品生产的核心。
- 水泥生产:水泥制造中的熟料烧成过程几乎完全在回转窑中进行。
- 颜料生产:用于制造二氧化钛(TiO2),一种常见的白色颜料。
- 活性炭:用于活性炭的初始生产和后续再生。
环境和废物管理
窑体实现完全燃烧和热分解的能力使其非常适合处理危险材料。
- 废物焚烧:在高温下安全处置工业废物、污水污泥甚至废旧轮胎。
- 土壤修复:加热受污染的土壤以解吸或销毁碳氢化合物等污染物。
- 资源回收:从炉渣中挥发锌和铅等有价金属,或回收废石灰以供再利用。
- 如果您的主要重点是生产水泥或石灰等大宗商品:回转窑是无可争议的行业标准,因为它在规模上具有无与伦比的效率、吞吐量和可靠性。
- 如果您的主要重点是处理多样化或敏感材料:窑体可调节的转速和精确的温度控制使其成为催化剂活化、矿石提纯或陶瓷加工的高度通用工具。
- 如果您的主要重点是环境修复或废物处理:窑体实现完全燃烧和均匀热解吸的能力使其成为销毁污染物和最小化废物量的强大而可靠的解决方案。
了解固有的权衡
虽然回转窑非常有效,但其设计和操作也存在明显的权衡,这一点至关重要。
高能耗
达到并维持超过 2000°C 的温度需要大量的燃料输入。这使得回转窑成为任何工业工厂中能源消耗最大的设备之一,代表着巨大的运营成本。
巨大的资本投资
回转窑是大型、重型且复杂的机器。初始购买价格,加上安装、基础工程和辅助设备(如燃烧器和密封件)的成本,构成了巨大的资本支出。
维护复杂性
高温、磨蚀性材料和持续旋转的结合创造了一个严苛的维护环境。耐火衬里必须定期更换,机械系统,特别是大型密封件和驱动机构,需要定期和专业的关注以防止故障。
为您的目标做出正确选择
使用回转窑的决定取决于热处理的具体要求。
最终,回转窑将强烈的热量与持续运动相结合的精湛技艺,使其成为现代材料转化不可替代的基石。
总结表:
| 应用类别 | 关键工艺 | 常见行业 |
|---|---|---|
| 矿物与矿石加工 | 煅烧、烧结、焙烧 | 水泥、石灰、金属 |
| 材料制造 | 水泥熟料烧成、颜料生产 | 建筑、化工 |
| 环境与废物 | 焚烧、土壤修复、资源回收 | 废物管理、回收 |
使用 KINTEK 的回转窑解决方案优化您的热处理!无论您是生产水泥、加工矿物还是管理危险废物,我们的实验室设备和耗材都旨在提供精确的温度控制、均匀加热和可靠的性能。让我们帮助您高效扩展运营 — 立即联系我们的专家,讨论您的具体需求!
图解指南