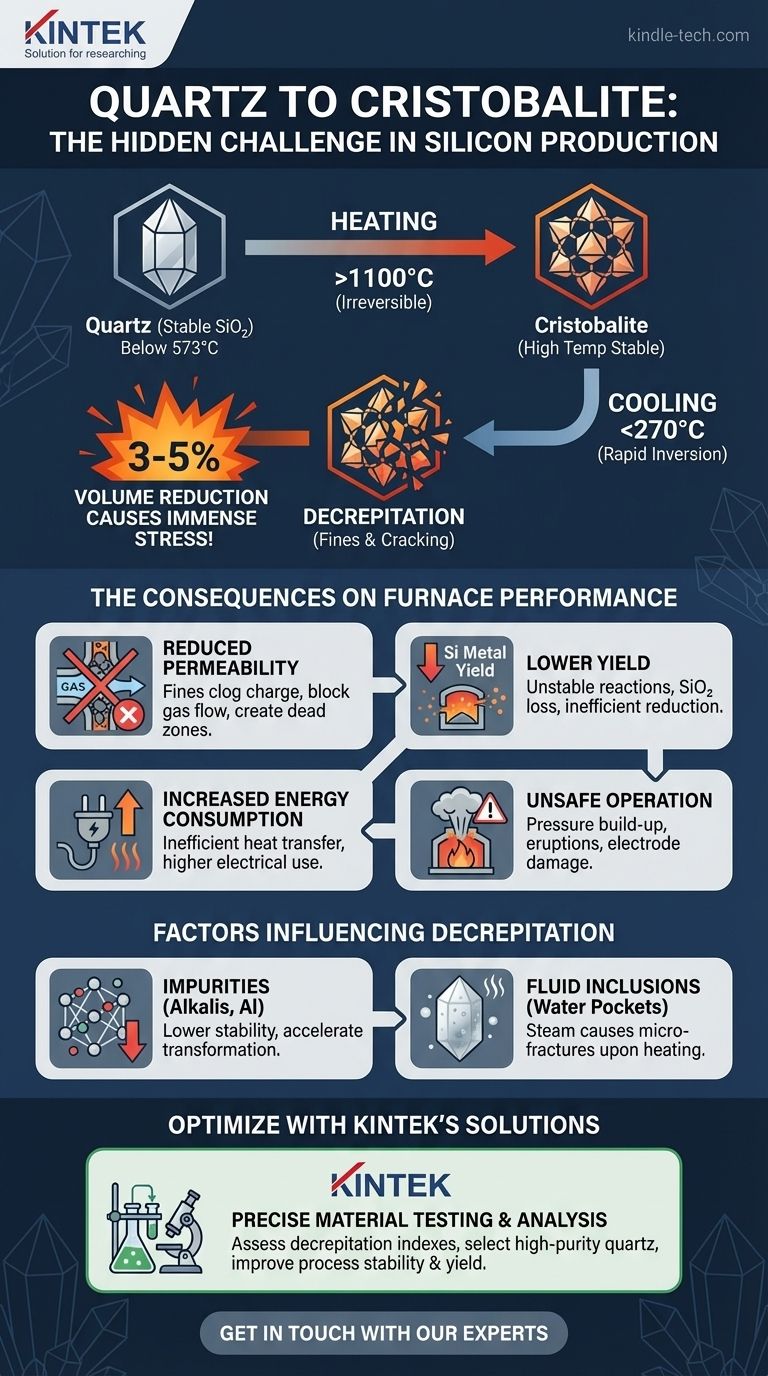
从根本上讲,在硅炉中加热石英会引发不可逆的相变,转化为方石英,这是一种不同晶型的二氧化硅(SiO₂)。这种转变,特别是方石英冷却时发生的快速体积变化,是原材料机械不稳定的主要驱动因素,直接影响炉子的效率、安全性以及硅的总产量。
在硅生产中使用石英的核心挑战并非加热本身,而是冷却循环的后果。转化为方石英引入了一种结构“记忆”,导致材料在冷却时破裂,产生细小颗粒,从而扰乱整个冶炼过程。
基本转化:石英到方石英
理解石英的行为首先要认识到,在硅炉的极端高温下,它并非惰性物质。它的晶体结构会发生深刻而永久的变化。
什么是石英?
石英是二氧化硅(SiO₂)在常温常压下稳定的晶体形式。在573°C以下以α-石英形式存在,高于此温度则可逆地转变为β-石英。这种初始转变只涉及微小的结构变化。
不可逆的高温变化
当炉内温度升至约1100°C以上时,石英结构开始缓慢且不可逆地重排为方石英,这是一种在极高温度下稳定的SiO₂多晶型物。虽然另一种相,鳞石英,也可能形成,但在这种工业背景下,方石英是更关键和常见的转化产物。
为什么方石英是关键角色
一旦形成,方石英在冷却时不会再变回石英。这意味着在炉子上部区域被加热到高温的石英块不再是石英;它们现在是方石英块。这种新材料具有完全不同的物理性质。

关键问题:方石英反转
形成方石英最显著的后果并非发生在峰值温度下,而是在炉料冷却期间。
高温方石英与低温方石英
与石英类似,方石英也有两种形式:高温β-方石英(在约270°C以上稳定)和低温α-方石英。这两种形式之间的转变是快速且可逆的。
不稳定的来源:突然的体积变化
当β-方石英冷却到约270°C以下时,它会瞬间反转为α-方石英。这种反转伴随着3-5%的突然且显著的体积收缩。这种快速收缩在材料内部产生巨大的内应力。
后果:爆裂
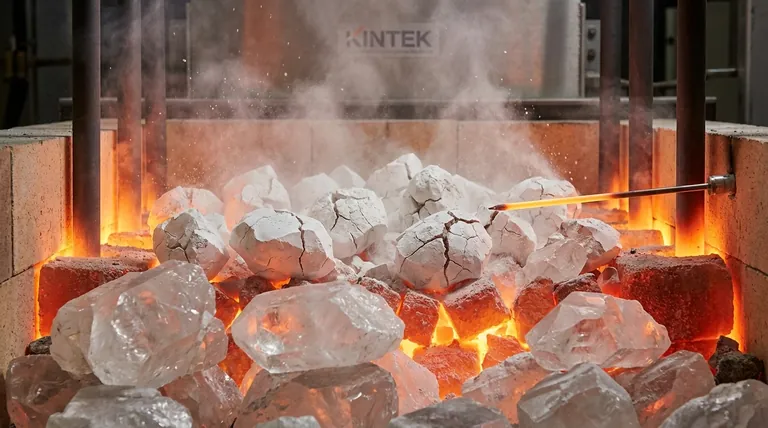
由α-β方石英反转引起的内应力通常过大,材料无法承受。结果是爆裂——石英块剧烈开裂、破碎并分解成更小的碎片和细小颗粒。可以将其想象成材料从内部自行破碎。
爆裂如何影响硅生产
细小颗粒的产生并非小问题;它从根本上降低了用于硅生产的埋弧炉的性能和稳定性。
对炉子渗透性的影响
硅炉依赖良好的渗透性,允许在炉膛中产生的热CO气体向上流动,预热并与下降的炉料发生反应。爆裂产生的细小颗粒会堵塞大块之间的空隙,从而大大降低这种渗透性。
这导致气体分布不均,形成气体流量过高的“通道”和气体流量过低的“死区”。
对反应性和产量的影响
细粉对产量有两个负面影响。首先,通道中强烈的气流可以将细小的SiO₂颗粒直接吹出炉外,这直接导致原材料的损失。
其次,不可预测的炉料移动和气流扰乱了稳定的反应区,导致SiO₂还原成硅金属的效率低下,并降低了整体工艺产量。
能源消耗增加
气体分布不良意味着传热效率低下。需要更多的能量来维持炉内所需的温度,从而增加电力消耗和运营成本。
不稳定和不安全的操作
堵塞的气流会导致炉料内部的气穴中压力升高。这种被困气体的突然释放可能导致“喷发”或“鼓风”,从而导致炉子运行极不稳定,可能损坏电极,并对人员造成重大的安全隐患。
理解权衡:并非所有石英都相同
特定石英源的爆裂倾向是一个关键的质量参数。这在很大程度上受材料纯度和内部结构的影响。
杂质的作用
石英晶格内的杂质,特别是碱金属(如钾和钠)和铝,充当助熔剂。它们降低了转化为方石英的能垒,使其发生得更快、温度更低,从而增加了爆裂程度。
流体包裹体的影响
“乳白色”或不透明的石英充满了微观流体包裹体,这些是微小的被困水滴。加热时,这些水变成高压蒸汽,从内部产生微裂纹。这削弱了结构,并严重加剧了爆裂的影响。高纯度、透明的石英通常表现更好。
评估热稳定性
由于这些因素,石英的“热稳定性”或“爆裂指数”是原材料选择的关键指标。这通常通过实验室测试来确定,该测试加热石英样品以模拟炉内条件并测量产生的细小物质的量。
通过石英选择优化您的工艺
深入了解石英转化使您能够通过管理主要原材料,从被动解决问题转向主动过程控制。
- 如果您的主要重点是最大限度地提高炉子稳定性和产量:优先采购具有经验证的低爆裂指数和最少流体包裹体含量的高纯度石英。
- 如果您的主要重点是管理多变的原材料供应:实施常规爆裂测试,对您的石英批次进行分类,并战略性地混合它们,以保持一致且可预测的炉料行为。
- 如果您的主要重点是降低能源成本:通过尽量减少使用易爆裂的石英来确保良好的炉料渗透性,因为这直接提高了气体分布和传热效率。
掌握您的SiO₂来源的行为是稳定、高效和盈利的硅生产操作的基础。
总结表:
| 阶段 | 关键变化 | 对硅生产的主要影响 |
|---|---|---|
| 加热(>1100°C) | 石英不可逆地转化为方石英。 | 为材料在冷却时不稳定性埋下伏笔。 |
| 冷却(<270°C) | 快速的α-β方石英反转,体积收缩3-5%。 | 导致爆裂(剧烈破碎),产生细小颗粒。 |
| 炉子操作 | 细粉堵塞炉料,降低渗透性并扰乱气流。 | 降低产量,增加能耗,并造成不安全条件。 |
通过掌握原材料行为,实现稳定高效的硅生产。石英在受热下的转化是炉子性能的关键因素。KINTEK专注于提供高纯度实验室设备和耗材,用于精确的材料测试和分析。我们的解决方案可帮助您准确评估石英爆裂指数,并优化原材料选择,以实现最大产量和操作安全。立即联系我们,讨论我们如何支持您的实验室在硅生产研发和质量控制方面的具体需求。
图解指南