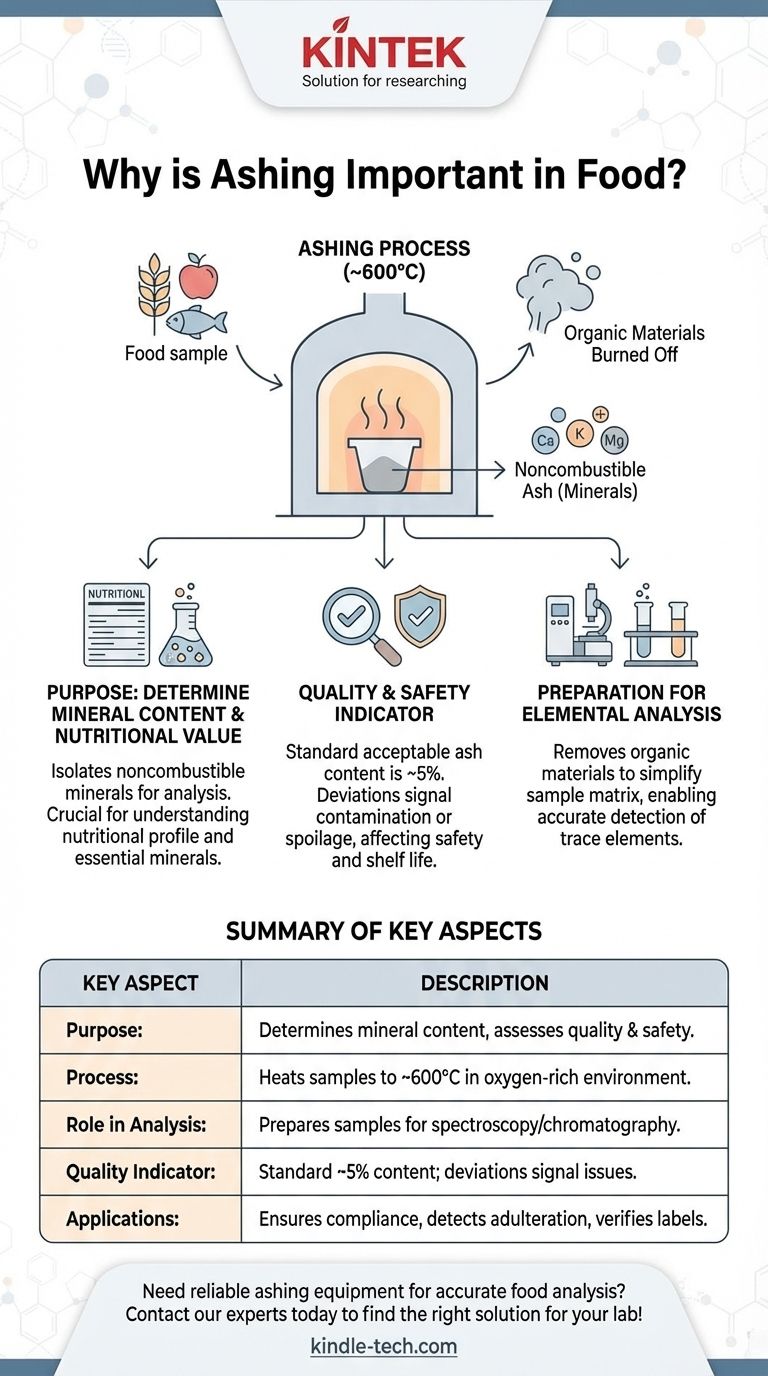
灰化是食品科学和分析化学中的一个关键过程,主要用于测定食品样品中的矿物质成分。通过在富氧环境中将样品加热到高温(约600°C),有机物质被燃烧殆尽,留下由氧化物和硫酸盐等矿物质组成的不可燃灰分。然后对这些灰分含量进行分析,以估算矿物质浓度,这对于评估食品质量、安全和营养价值至关重要。灰化也作为进一步元素分析(如光谱法或色谱法)的预处理步骤,通过去除不必要的有机物质来确保结果的准确性。保持适当的灰分含量(通常约为5%)对于食品质量控制至关重要,因为偏差可能表明污染或老化等问题。
关键点解释:
-
灰化在食品分析中的目的:
- 灰化主要用于测定食品样品中的矿物质含量。通过燃烧掉有机物质,该过程分离出不可燃矿物质,然后对其进行分析以估算其浓度。
- 这对于了解食品的营养成分至关重要,因为钙、钾和镁等矿物质对人体健康必不可少。
-
干灰化过程:
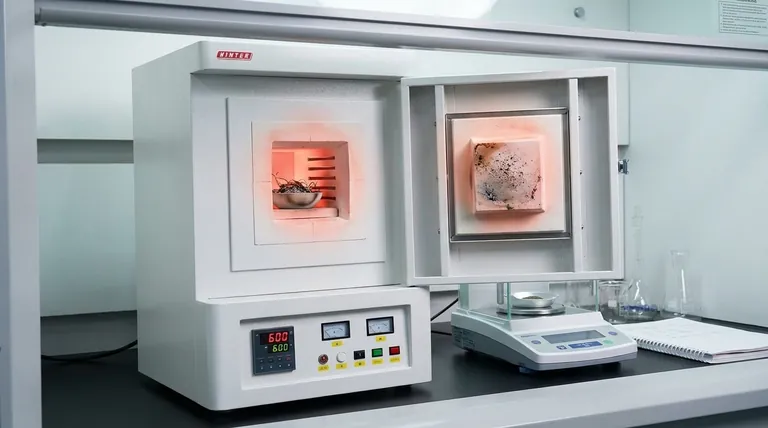
- 样品在灰化炉中,在氧气存在下,加热到约600°C(1112°F)的温度。
- 有机成分被氧化和挥发,留下无机矿物质,形式为氧化物、硫酸盐和其他化合物。
- 称量剩余的灰分,根据干重灰分含量确定矿物质含量。
-
在元素分析中的作用:
- 灰化是进一步元素分析技术(如光谱法或色谱法)的初步步骤。
- 通过去除有机物质,灰化简化了样品基质,使其更容易检测和量化微量元素。
-
在食品质量和安全中的重要性:
- 灰分含量是食品质量的关键指标。标准可接受的灰分含量约为5%,偏离此值可能表明污染或变质等问题。
- 较高的灰分含量可能表明存在无机污染物或食品产品老化,这会影响安全性和保质期。
-
在食品行业中的应用:
- 灰化广泛应用于食品行业,以确保符合法规标准并保持产品一致性。
- 它有助于评估成分的纯度、检测掺假以及验证食品标签上的营养声明。
-
与分析化学的联系:
- 灰化是一种矿化形式,它预浓缩微量物质以进行更准确的化学分析。
- 此过程对于光学分析(例如光谱法)和分离方法(例如色谱法)等技术至关重要,因为有机物质的存在可能会干扰结果。
-
对食品采购商的实际意义:
- 对于设备和耗材采购商而言,了解灰化的重要性可以指导选择合适的灰化炉和相关分析工具。
- 确保设备能够达到并保持所需的温度和氧气流量对于准确测定灰分含量至关重要。
通过了解灰化在食品分析中的作用,利益相关者可以更好地认识其在确保食品质量、安全和符合行业标准方面的重要性。这些知识还有助于就准确可靠的矿物质分析所需的设备和耗材做出明智的决策。

总结表:
| 关键方面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 目的 | 测定矿物质含量并评估食品质量、安全和营养价值。 |
| 过程 | 在富氧环境中将样品加热至约600°C,以燃烧掉有机物质。 |
| 在分析中的作用 | 通过去除有机物质,为光谱法或色谱法准备样品。 |
| 质量指标 | 标准灰分含量(约5%)表明食品质量;偏差表示污染。 |
| 应用 | 确保合规性、检测掺假并验证营养声明。 |
| 设备注意事项 | 需要精确的温度控制和氧气流量才能获得准确结果。 |
需要可靠的灰化设备进行准确的食品分析吗?立即联系我们的专家,为您的实验室找到合适的解决方案!
图解指南