从本质上讲,溅射是一个物理过程,用于将极其薄且均匀的材料层沉积到表面上。它的工作原理是在真空中产生等离子体,并利用来自该等离子体的带电离子,物理地将材料源(称为“靶材”)上的原子撞击下来。这些被撞击下来的原子然后传输并覆盖到目标物体或“基板”上,形成一层高度受控的薄膜。
溅射不仅仅是“喷射”原子。它是一种高度受控的真空沉积技术,其中惰性气体被电离以产生等离子体。然后将这些离子加速轰击靶材,通过物理动量传递将原子撞击下来,这些原子随后沉积到基板上以形成精确的薄膜。
溅射过程的结构
要了解溅射的工作原理,您必须首先认识到其在精心控制的环境中运行的关键组成部分。
真空室
整个过程发生在密闭的真空室内。去除空气和其他反应性气体对于防止薄膜污染以及使溅射的原子能够从靶材自由传输到基板至关重要。
靶材
靶材是您希望沉积的材料的固体块。它充当薄膜的来源。在靶材上施加高压负电荷,使其成为阴极。
基板
这是将被涂覆的物体或材料。它被战略性地放置,以拦截从靶材喷射出的原子流。
溅射气体
一种惰性气体,最常见的是氩气 (Ar),以极低的压力引入腔室。这种气体不是最终薄膜的一部分;相反,它充当轰击过程的“弹药”。
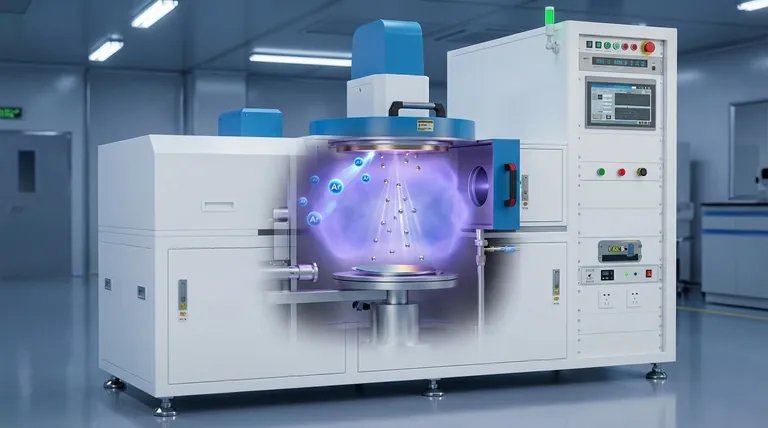
溅射机制,分步解析
该过程按精确的顺序展开,将固体靶材转化为原子蒸汽,从而构建新薄膜。
步骤 1:产生等离子体
引入氩气后,会施加一个强大的电场。腔室中的自由电子被这个电场加速,并与中性氩原子碰撞,将一个电子从氩原子上撞击下来。
这会产生一个带正电的氩离子 (Ar+) 和另一个自由电子,后者可以电离更多的氩原子。这种连锁反应会维持一种发光的、带电的物质状态,称为等离子体——它是正离子、电子和中性原子的混合物。
步骤 2:离子轰击
带正电的氩离子 (Ar+) 被带负电的靶材强烈吸引。它们以高速加速冲向靶材,获得显著的动能。
步骤 3:通过动量传递实现原子喷射
当这些高能离子撞击靶材表面时,它们会以类似于台球碰撞的过程将其动量传递给靶材原子。这种初始撞击会在靶材材料的前几个原子层内引发一个碰撞级联。
如果这个级联将足够多的能量导向表面——一个大于材料表面结合能的量——一个靶材原子就会被物理地撞击松动并从表面喷射出来。这个被喷射出的原子就是我们所说的“溅射”出来的。
步骤 4:沉积和薄膜生长
溅射出的原子在真空中沿直线传播,直到撞击到基板上。到达后,它们会粘附在表面上(称为吸附)并开始一层一层地堆积。
随着时间的推移,这些原子的积累会在基板表面形成一层连续、致密且高度附着的薄膜。
理解权衡和控制因素
溅射薄膜的最终性能并非偶然;它们是控制关键工艺参数的直接结果。理解这些权衡对于实现期望的结果至关重要。
气体压力
降低气体压力会减少溅射原子在到达基板的途中与气体原子碰撞的机会。这会形成更致密、质量更高的薄膜,但通常会降低沉积速率。相反,较高的压力可能会提高沉积速率,但可能导致薄膜孔隙率增加。
靶材功率和电压
增加施加到靶材上的电压(以及功率)会增加轰击离子的能量。这会提高溅射产额——每个入射离子喷射出的原子数量——从而提高沉积速率。然而,过高的功率可能会导致基板和靶材不必要的发热。
气体选择
惰性气体离子的质量会影响动量传递的效率。像氪 (Kr) 或氙 (Xe) 这样的较重气体比氩气更有效地溅射较重的靶材材料,从而实现更高的沉积速率。然而,它们的成本也明显更高。
系统几何形状
靶材与基板之间的距离和方向对薄膜的均匀性和厚度有很大影响。较短的距离可以提高速率,但可能会降低大面积基板的均匀性。
将其应用于您的目标
溅射的多功能性来自于您调整这些参数以实现特定结果的能力。
- 如果您的主要重点是高沉积速率: 增加施加到靶材上的功率,并考虑使用像氪这样的较重惰性气体以最大化动量传递。
- 如果您的主要重点是薄膜质量和密度: 使用较低的气体压力以确保溅射原子能够清晰传输,并精确控制基板温度。
- 如果您的主要重点是涂覆复杂合金: 溅射是理想的选择,因为物理喷射机制通常能保持靶材到薄膜的元素比例。
- 如果您的主要重点是附着力: 溅射提供了出色的薄膜附着力,因为到达的原子具有足够的能量稍微嵌入基板表面,形成牢固的粘合。
通过掌握这些核心原理,您可以利用溅射技术在原子级别上设计具有特定光学、电学或机械特性的表面。
总结表:
| 关键组件 | 在溅射过程中的作用 |
|---|---|
| 真空室 | 提供无污染的环境供原子传输。 |
| 靶材(阴极) | 被轰击以释放涂层原材的源材料。 |
| 基板 | 接收薄膜涂层的物体或表面。 |
| 溅射气体(例如,氩气) | 被电离以产生用于轰击靶材的等离子体。 |
| 等离子体 | 离子和电子的混合物,为溅射过程提供能量。 |
准备好利用精密薄膜来设计表面了吗? KINTEK 专注于溅射和其他沉积技术的实验室设备和耗材。我们的专业知识可帮助实验室实现卓越的薄膜附着力、密度和均匀性。无论您是开发半导体、光学涂层还是先进材料,我们都能提供您所需的可靠设备和支持。立即联系我们的专家,讨论您的具体应用,并发现 KINTEK 如何增强您的研发或生产能力。
图解指南

相关产品
- RF PECVD 系统 射频等离子体增强化学气相沉积 RF PECVD
- 倾斜旋转等离子体增强化学气相沉积 PECVD 设备管式炉
- 化学气相沉积CVD设备系统腔体滑动PECVD管式炉带液体气化器PECVD设备
- VHP灭菌设备过氧化氢H2O2空间灭菌器
- 实验室用多边形压制模具



















