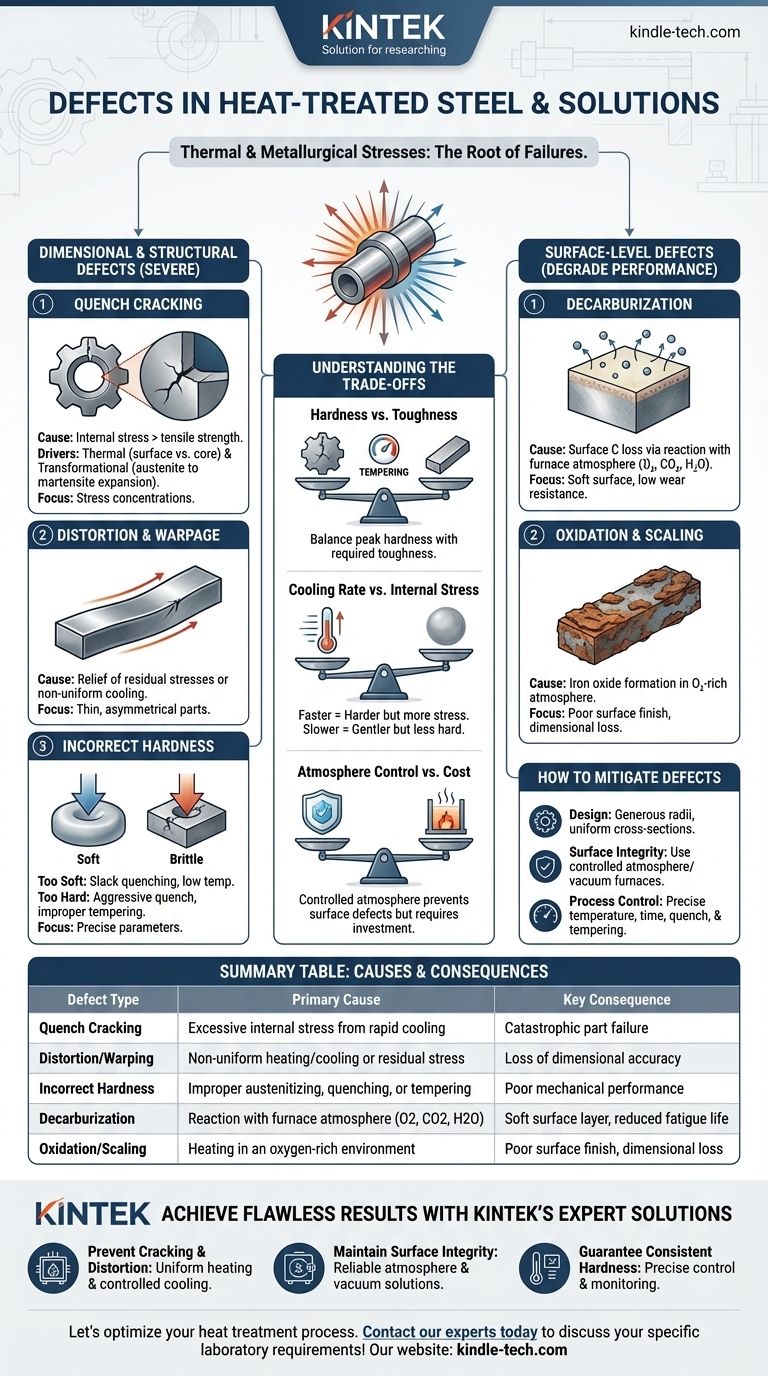
热处理钢材的缺陷主要由加热和快速冷却过程中产生的巨大热应力及金相应力引起。最常见的缺陷是开裂、变形(翘曲)、不良的表面变化(如脱碳和氧化皮),以及未能达到目标硬度或显微组织。这些失效并非随机发生,而是工艺参数控制不当的直接后果。
热处理缺陷是热应力、相变和大气化学反应的可预测结果。预防这些缺陷的关键在于严格控制温度变化速率、炉内气氛以及从设计阶段开始的零件几何形状。
尺寸和结构失效
最严重的缺陷会损害部件的机械完整性和尺寸精度,常常使其无法使用。
淬火裂纹
淬火裂纹是最关键的热处理缺陷。当淬火产生的内应力超过材料的极限抗拉强度时,就会发生淬火裂纹。
这主要由两种力驱动:来自表面冷却速度远快于核心的热应力,以及奥氏体转变为脆性马氏体时发生的膨胀所产生的相变应力。
裂纹通常起源于应力集中点,如尖角、键槽或零件截面的突然变化处。
变形和翘曲
变形是部件在热处理过程中尺寸或形状发生的不可逆变化。
这通常是由于先前制造步骤(如机械加工)中产生的残余应力释放,或由于不均匀的加热和冷却所致。薄、长或不对称的零件特别容易发生翘曲。
硬度不正确
获得正确的硬度通常是主要目标,而在此方面的失败可能由多种因素造成。
零件过软可能是由于奥氏体化温度或时间不足,或者淬火速度对于钢的淬透性来说过慢(称为不完全淬火)。
相反,零件过硬且脆通常是由于淬火过于剧烈,或者更常见的是在硬化后退火步骤不当或遗漏。

表面缺陷
这些缺陷会降低钢材表面质量,损害其在需要高耐磨性或疲劳强度的应用中的性能。
脱碳
脱碳是钢材表面碳的流失。这是一个严重的问题,因为碳是钢材硬度的主要决定元素。
它是由钢材与炉内气氛(氧气、二氧化碳、水蒸气)在高温下发生化学反应引起的。结果是形成一层柔软、薄弱的表面层,这会大大降低耐磨性和疲劳寿命。
氧化和氧化皮
氧化是在富氧气氛中加热时,部件表面形成一层氧化铁(氧化皮)。
这种氧化皮会导致表面光洁度差和尺寸精度损失。它还可能对零件起到隔热作用,导致淬火不均匀,并可能掩盖更严重的潜在缺陷,如淬火裂纹。
理解权衡
选择热处理工艺总是涉及平衡相互竞争的因素。理解这些权衡是预防缺陷的关键。
硬度与韧性
热处理中最基本的权衡是,产生极高硬度的工艺(如淬火)也会产生脆性显微组织(未回火马氏体)。
回火是淬火后必不可少的步骤,它能降低这种脆性和内应力,赋予韧性。然而,这个过程也会降低峰值硬度。关键在于找到应用所需的精确平衡点。
冷却速率与内应力
更快的冷却速率在实现完全硬度方面更有效,尤其是在低合金钢中。
然而,快速淬火(例如,使用水或盐水)会产生巨大的热梯度和内应力,大大增加变形和开裂的风险。较慢的淬火(例如,使用油或气体)更为温和,但可能无法达到最大硬度。
气氛控制与成本
使用受控气氛(如真空、氮气或氩气)可以完全防止脱碳和氧化,从而获得清洁、光亮的零件。
然而,与在露天炉中加热相比,这些工艺需要更复杂和昂贵的设备。成本必须由部件的表面要求来证明。
如何减轻热处理缺陷
预防缺陷需要一种系统的方法,侧重于设计、材料选择和精确的工艺控制。
- 如果您的主要重点是防止开裂和变形: 设计具有大圆角和均匀截面的零件,并选择适合钢材淬透性的较温和的淬火介质。
- 如果您的主要重点是保持表面完整性: 利用受控气氛炉(例如,真空、惰性气体)或保护涂层来防止脱碳和氧化皮。
- 如果您的主要重点是实现一致的硬度: 确保精确控制奥氏体化温度、保温时间和淬火搅拌,并始终进行适当的回火循环。
成功的热处理是一个受控的工程过程,设计中的远见和执行中的精确性决定了部件的最终质量。
总结表:
| 缺陷类型 | 主要原因 | 主要后果 |
|---|---|---|
| 淬火裂纹 | 快速冷却产生的过大内应力 | 灾难性零件失效 |
| 变形/翘曲 | 不均匀加热/冷却或残余应力 | 尺寸精度损失 |
| 硬度不正确 | 奥氏体化、淬火或回火不当 | 机械性能差 |
| 脱碳 | 与炉内气氛(O2、CO2、H2O)反应 | 表面软层,疲劳寿命降低 |
| 氧化/氧化皮 | 在富氧环境中加热 | 表面光洁度差,尺寸损失 |
KINTEK 的专业解决方案助您实现完美结果
消除昂贵的热处理缺陷,确保您的钢部件达到硬度、耐用性和尺寸精度的最高标准。KINTEK 专注于优质实验室设备和耗材,提供您的实验室完善热处理所需的精密炉具、气氛控制系统和专家支持。
我们助您:
- 防止开裂和变形: 采用专为均匀加热和受控冷却设计的设备。
- 保持表面完整性: 通过可靠的气氛控制和真空炉解决方案。
- 保证硬度一致: 采用精确的温度控制和监测工具。
让我们优化您的热处理工艺。立即联系我们的专家,讨论您的具体实验室需求!
图解指南