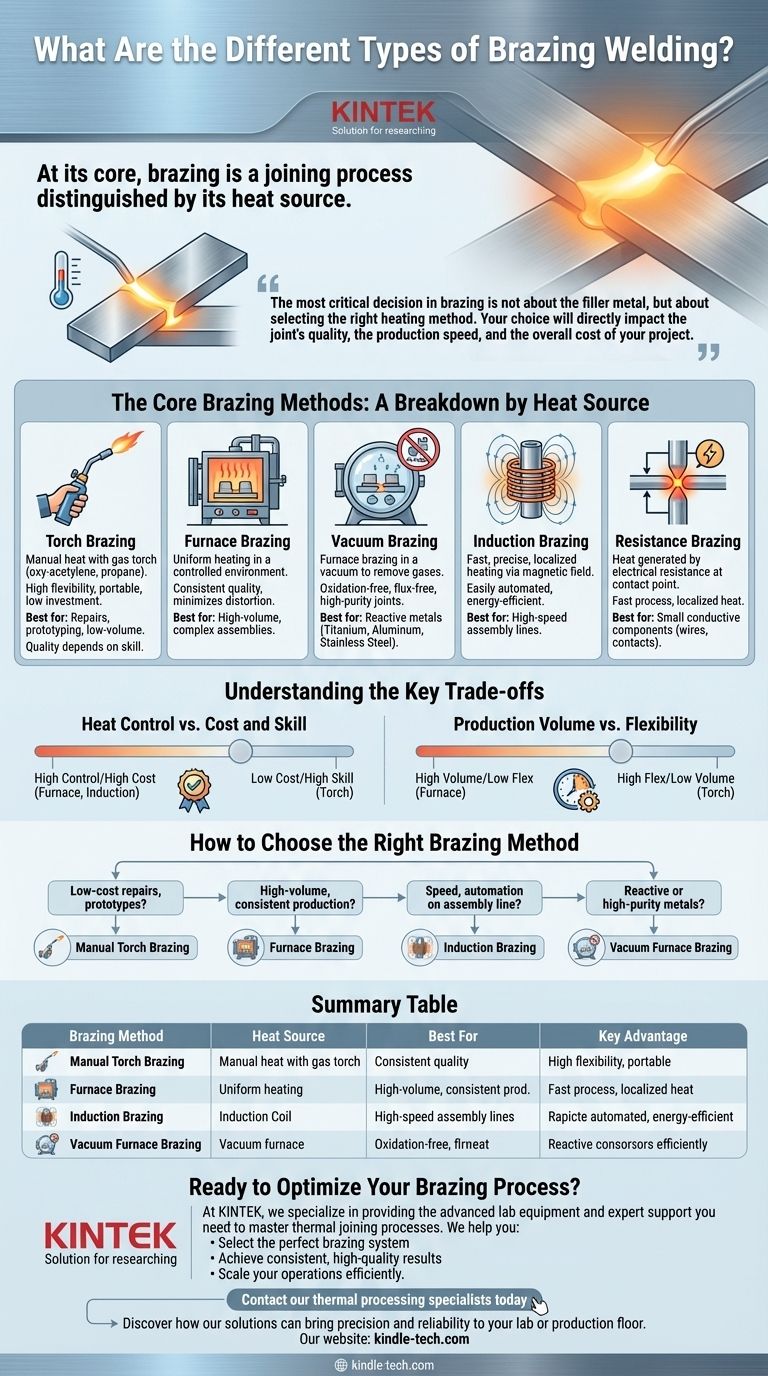
从核心来看,钎焊是一种连接工艺,其特点在于其热源。虽然常与焊接混淆,但钎焊使用熔点低于母材的填充金属来连接金属,从而在不熔化零件本身的情况下形成牢固的结合。钎焊的主要类型是根据施加热量的方法来定义的,包括火焰、炉中、感应和电阻钎焊。
钎焊中最关键的决定不是关于填充金属,而是选择正确的加热方法。您的选择将直接影响接头的质量、生产速度以及项目的总成本。
核心钎焊方法:按热源分类
钎焊方法几乎总是根据其产生和施加热量的方式进行分类。每种方法在速度、成本、精度以及对不同材料和生产量的适用性方面都提供了独特的特点。
火焰钎焊
这是最常见和最通用的钎焊形式。它涉及使用燃气焊枪(如氧乙炔或丙烷)手动加热零件并将填充合金熔化到接头中。
它具有高度便携性,初始投资低,非常适合维修、原型制作和小批量生产。然而,质量高度依赖于操作员的技能。
炉中钎焊
在炉中钎焊中,将组件(预先放置好填充金属)装入高温炉中。整个组件在受控环境中均匀加热至钎焊温度。
这种方法非常适合复杂组件的大批量生产,因为它能以最小的变形生产出一致、高质量的接头。它确保即使是难以触及的接头也能均匀受热。
真空钎焊
真空钎焊是一种特殊类型的炉中钎焊。该过程在真空中进行,可去除可能污染或氧化金属的氧气和其他气体。
这对于连接钛、铝和不锈钢等活性金属以及创建清洁、无助焊剂的接头至关重要。它是航空航天、医疗和半导体行业的标准。
感应钎焊
这种方法使用感应线圈产生的交变磁场来加热导电金属零件。加热速度极快、精确且局限于接头区域。
感应钎焊易于自动化且可重复性高,使其成为高速装配线的首选。它还具有能源效率,因为它只加热需要连接的零件部分。
电阻钎焊
电阻钎焊通过电流流过接头时产生的电阻来产生热量,通常通过碳电极。热量集中在接触点。
这是一种快速工艺,适用于连接小型、高导电性组件。它通常用于连接对局部加热要求严格的电气触点和电线。

了解关键权衡
选择钎焊方法涉及平衡相互冲突的优先事项。了解这些权衡对于做出符合您的技术和业务目标的明智决策至关重要。
热量控制与成本和技能
精确的热量控制是获得高质量钎焊接头最重要的因素。
炉中和感应钎焊提供卓越的自动化控制,但资本成本高。火焰钎焊成本低廉,但热量管理的责任完全落在熟练的操作员身上。
生产量与灵活性
您的所需产量决定了您的选择。炉中钎焊专为相同零件的大规模生产而设计,但由于加热和冷却周期长,对于一次性作业效率非常低。
火焰钎焊为独特的维修或原型制作提供了最大的灵活性,但无法与自动化方法在大批量生产中的速度和可重复性相媲美。
材料和气氛纯度
您正在连接的母材可能会立即排除某些方法。许多高强度合金和活性金属在高温下暴露于氧气会变弱或受损。
对于这些材料,火焰钎焊不是一个选择。需要受控气氛,因此在真空或惰性气体(如氮气或氩气)中进行炉中钎焊是唯一可行的选择。
如何选择正确的钎焊方法
您的具体应用和目标将引导您选择正确的方法。使用这些指南来缩小您的选择范围。
- 如果您的主要关注点是低成本维修或一次性原型:手动火焰钎焊提供了灵活性和低初始投资的最佳组合。
- 如果您的主要关注点是大批量、一致性生产:炉中钎焊是大规模生产可靠接头的行业标准。
- 如果您的主要关注点是装配线上的速度和自动化:感应钎焊提供无与伦比的速度和精确、可重复的局部加热。
- 如果您的主要关注点是连接活性或高纯度金属(例如,钛、不锈钢):真空炉中钎焊是必不可少的,以防止氧化并确保接头完整性。
最终,掌握热源的选择是成功钎焊操作最关键的一步。
总结表:
| 钎焊方法 | 热源 | 最适合 | 主要优点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 火焰钎焊 | 燃气焊枪 | 维修、原型制作、小批量 | 成本低、灵活性高 |
| 炉中钎焊 | 受控炉 | 大批量、复杂组件 | 质量一致、加热均匀 |
| 真空钎焊 | 真空炉 | 活性金属(钛、不锈钢) | 无氧化、高纯度接头 |
| 感应钎焊 | 电磁感应 | 自动化装配线 | 快速、精确、局部加热 |
| 电阻钎焊 | 电阻 | 小型导电组件 | 局部加热、工艺快速 |
准备好优化您的钎焊工艺了吗?
选择正确的钎焊方法对于在您的金属组件中实现坚固、可靠的接头至关重要。在 KINTEK,我们专注于提供您掌握热连接工艺所需的先进实验室设备和专家支持。
我们帮助您:
- 为您的特定材料和生产量选择完美的钎焊系统
- 通过精确的温度控制和气氛管理实现一致、高质量的结果
- 从原型制作到大批量生产,高效扩展您的运营
无论您是使用活性合金还是需要自动化解决方案,KINTEK 都拥有提升您钎焊能力的设备和专业知识。
立即联系我们的热处理专家,讨论您的项目要求,并了解我们的解决方案如何为您的实验室或生产车间带来精度和可靠性。
图解指南