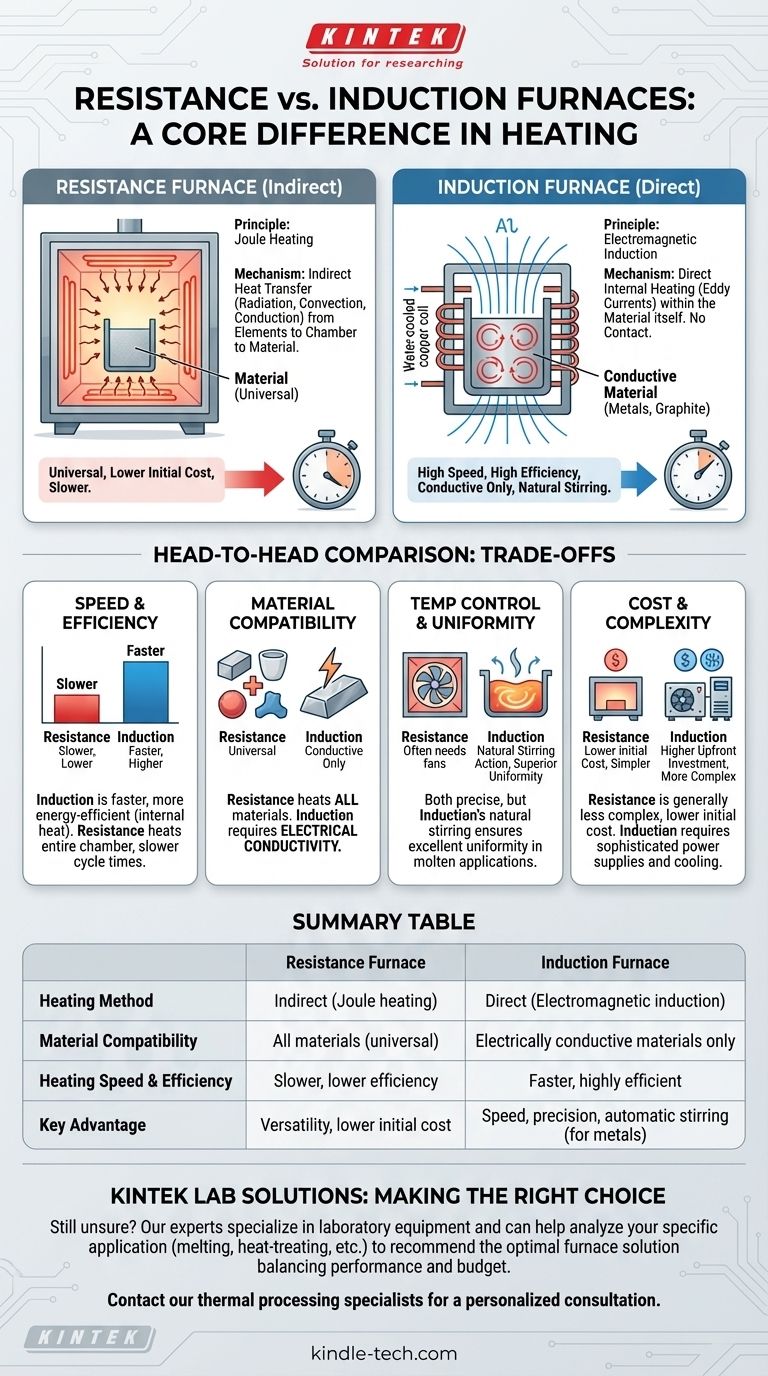
电阻炉和感应炉的根本区别在于它们的加热方法。电阻炉使用加热元件发热,然后间接将热量传递给材料,这很像传统的烤箱。相比之下,感应炉利用电磁场直接在导电材料内部产生热量,无需物理接触。
这两种技术之间的核心选择归结为多功能性与效率之间的权衡。电阻炉是加热任何材料的通用工具,而感应炉则是针对金属等导电材料的高速、高效专家。
电阻炉的工作原理
电阻炉是最常见、最直接的电炉类型,其工作原理与使用烤面包机或电炉的人所熟悉的原理相同。
原理:焦耳加热
其机制基于电阻。高电流通过由高电阻材料制成的特殊设计的加热元件。
这种对电流流动的电阻导致元件变得极热,这种效应被称为焦耳加热。
机制:间接热传递
这些元件产生的强烈热量随后传递给炉内的材料。这通过辐射、对流和传导的组合发生。
本质上,炉子加热炉膛的空气和炉壁,然后炉膛和炉壁再加热目标材料。这是一种间接加热过程。
主要特点
电阻炉以其多功能性而闻名,因为它们可以加热任何类型的材料,无论其是否导电。它们通常设计更简单,前期成本更低。

感应炉的工作原理
感应加热是一种更先进、更有针对性、更高效的方法,它从根本上改变了热能传递给材料的方式。
原理:电磁感应
感应炉使用强大的线圈产生快速交变的磁场。当导电材料(如钢或石墨)置于此磁场中时,磁场会在材料本身内部感应出电流。
这些小的环形电流被称为涡流。
机制:直接内部加热
材料对这些涡流的固有电阻会从内到外产生精确而快速的热量。不需要外部加热元件。
热量直接在工件内部产生,这使得过程极其快速和高效,因为很少有能量浪费在加热周围空间上。
主要特点
感应加热熔融金属的一个独特优点是磁场引起的自然搅拌作用。这确保了优异的温度均匀性和合金混合,无需机械搅拌器。
了解权衡:正面比较
选择合适的炉子需要了解每种加热方法固有的独特优势和局限性。
加热速度和效率
感应炉明显更快,能效更高。由于热量在内部产生,达到目标温度所需的时间大大缩短,并且更少的能量损失到环境中。
电阻炉必须首先加热元件和整个炉膛,导致循环时间较慢,整体效率较低。
材料兼容性
电阻炉是通用的。它们可以加热金属、陶瓷、聚合物和复合材料,因为它们的操作不依赖于材料的电学特性。
感应炉是专家。它们非常有效,但只能加热导电材料。
温度控制和均匀性
这两种类型都可以实现高水平的温度控制。然而,感应炉中的自然搅拌效应在熔融金属应用中提供了卓越的热均匀性。
在电阻炉中,实现高均匀性通常需要风扇来循环空气,这增加了复杂性。
成本和复杂性
电阻炉通常结构更简单,初始成本更低。它们的维护通常更简单,并且在其使用寿命内成本更低。
感应炉是更复杂的系统,需要精密的电源和冷却系统,这导致更高的前期投资。
为您的应用做出正确选择
您的最终决定应完全根据您的具体材料、工艺要求和预算来指导。
- 如果您的主要关注点是多功能性和较低的初始成本:电阻炉是更好的选择,可作为各种材料和应用的可靠主力。
- 如果您的主要关注点是速度、能源效率和加工导电金属:感应炉提供无与伦比的性能,特别适用于熔化、钎焊或高速热处理。
- 如果您正在使用陶瓷等非导电材料:电阻炉是您唯一可行的选择。
- 如果您需要自动搅拌熔融金属浴:感应炉固有的电磁搅拌是一个主要的运行优势。
了解加热机制的这一根本区别是选择最有效的工具来完成您的特定热处理任务的关键。
总结表:
| 特点 | 电阻炉 | 感应炉 |
|---|---|---|
| 加热方法 | 间接(焦耳加热) | 直接(电磁感应) |
| 材料兼容性 | 所有材料(通用) | 仅限导电材料 |
| 加热速度和效率 | 较慢,效率较低 | 较快,效率高 |
| 主要优势 | 多功能性,较低的初始成本 | 速度、精度、自动搅拌(用于金属) |
仍然不确定哪种炉子适合您实验室的特定材料和工艺?
KINTEK 专注于实验室设备和耗材。我们的专家可以帮助您分析您的应用要求——无论您是熔化金属、热处理合金还是加工陶瓷——以推荐最佳的炉子解决方案,平衡性能、效率和预算。
立即联系我们的热处理专家,进行个性化咨询,了解合适的炉子如何提高您实验室的生产力和成果。
图解指南