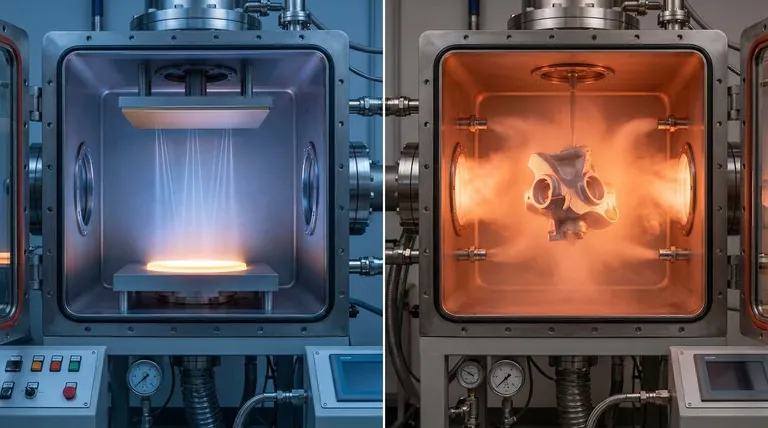
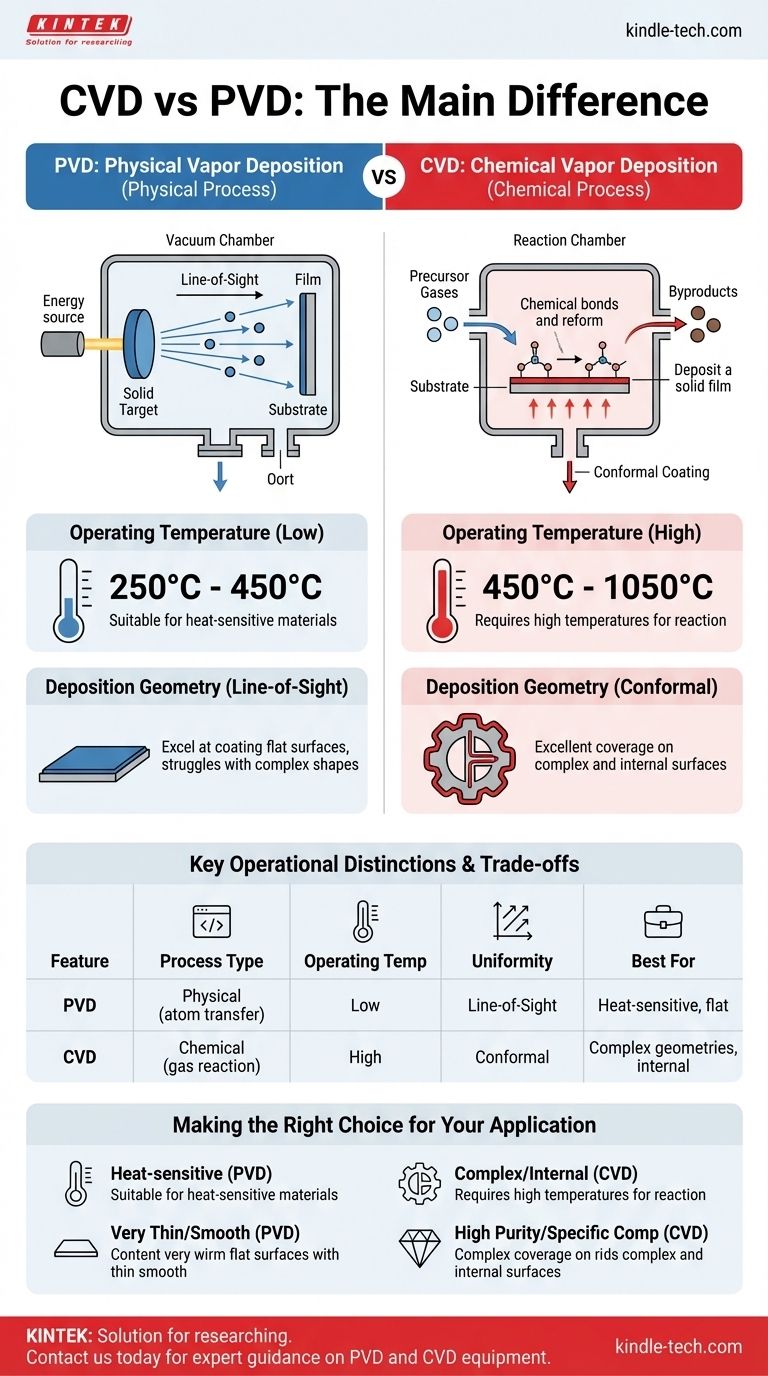
CVD和PVD的主要区别在于源材料的状态和沉积过程的性质。物理气相沉积(PVD)是一种物理过程,它将固体材料汽化,然后汽化后的物质沿直线移动并凝结到基材上。相比之下,化学气相沉积(CVD)是一种化学过程,它使用前体气体在基材表面直接发生反应,形成所需的固体薄膜。
PVD是一种“视线”物理过程,很像用原子喷漆,这使其非常适合在较低温度下进行表面涂层。CVD是一种化学反应过程,气体包围组件,使其能够均匀地涂覆复杂形状,但这需要更高的温度。
了解核心机制
PVD和CVD都是先进的真空沉积技术,用于在表面形成薄而功能性的薄膜。然而,它们形成薄膜的方式从根本上是不同的。
PVD:一种物理的、视线过程
在PVD中,涂层材料以固体靶材的形式存在于真空室中。这个固体受到能量(如离子束)的轰击,物理性地剥离原子并使其汽化。
这些汽化后的原子沿直线——“视线”——移动,直到它们撞击基材并凝结,形成薄的固体薄膜。材料本身没有发生化学变化。
CVD:一种化学反应过程
在CVD中,过程始于挥发性前体气体。这些气体被引入含有基材的反应室中。
反应室被加热到高温,为气体之间以及气体与基材表面之间的反应提供能量。这种化学反应导致固体薄膜的沉积,同时其他化学副产品被排出反应室。
关键操作区别
PVD和CVD之间的机械差异导致了它们在操作和应用上的关键区别。
操作温度
PVD在相对较低的温度下运行,通常在250°C到450°C之间。这使其适用于更广泛的基材材料,包括一些对热敏感的材料。
CVD需要显著更高的温度来驱动必要的化学反应,通常从450°C到1050°C。这种高温限制了其在能够承受这种极端条件而不会变形或熔化的基材上的使用。
沉积几何形状
由于PVD是一种视线过程,它擅长涂覆平面或物体的暴露表面。然而,它难以均匀涂覆复杂形状、内部通道或组件的底面,因为存在“阴影”效应。
CVD的气态性质意味着前体分子会包围整个部件。这使其能够在复杂的几何形状甚至复杂的内部结构上形成高度均匀或共形涂层。它还允许在单个批次中同时涂覆多个部件。
薄膜特性
PVD通常会产生非常薄、光滑和致密的涂层。该工艺可以精细控制薄膜的结构和耐用性。
CVD可以生产更广泛的薄膜厚度,从非常薄到相当厚。由于化学反应过程,涂层非常纯净,但有时可能比PVD生产的涂层更粗糙。
了解权衡
没有哪种方法是普遍优越的;选择涉及根据应用要求进行一系列明确的权衡。
PVD:低温优势
PVD的关键优势在于其较低的加工温度。这使其可用于某些钢合金、铝甚至某些聚合物等材料,这些材料会被CVD的高温破坏。
主要限制是其视线性质。在具有复杂几何形状的部件上实现均匀涂层,例如螺纹或精细模具,是极其困难的。
CVD:以成本为代价的卓越覆盖
CVD能够在任何暴露表面上沉积均匀薄膜是其最大的优势,使其成为涂覆管道内部或复杂机器部件的唯一选择。
其主要缺点是所需的高温。这种高热预算严重限制了兼容基材材料的列表,有时还会改变基材本身的性能。
为您的应用做出正确选择
您在PVD和CVD之间的选择完全取决于您的基材材料、部件的几何形状以及最终薄膜所需的特性。
- 如果您的主要关注点是涂覆热敏材料: PVD是正确的选择,因为它具有更低的运行温度。
- 如果您的主要关注点是在复杂的3D形状或内表面上实现均匀涂层: CVD更优越,因为其气态前体可以到达所有暴露区域。
- 如果您的主要关注点是在相对平坦的物体上获得非常薄、光滑且耐用的表面: PVD通常能为这些应用提供更好的控制和更光滑的表面。
- 如果您的主要关注点是高薄膜纯度或不易作为固体靶材获得的特定化学成分: CVD通过其前体气体的化学性质提供更大的灵活性。
最终,了解这些核心机械和操作差异使您能够选择与您的工程目标完美契合的沉积技术。
总结表:
| 特点 | PVD(物理气相沉积) | CVD(化学气相沉积) |
|---|---|---|
| 工艺类型 | 物理(原子转移) | 化学(气体反应) |
| 操作温度 | 250°C - 450°C(低) | 450°C - 1050°C(高) |
| 涂层均匀性 | 视线(可能存在阴影) | 共形(复杂形状上均匀) |
| 最适合 | 热敏材料,平面 | 复杂几何形状,内表面 |
仍然不确定哪种沉积方法适合您的应用? KINTEK的专家随时为您提供帮助!
我们专注于为您的所有涂层需求提供先进的实验室设备和耗材。无论您是使用需要PVD低温优势的热敏材料,还是需要CVD卓越覆盖的复杂几何形状,我们的团队都能为您提供完美的解决方案。
立即联系我们,讨论您的具体要求,并了解我们的专业知识如何提升您实验室的能力。立即联系我们的专家!
图解指南
相关产品
- HFCVD设备用于拉丝模具纳米金刚石涂层
- 用于层压和加热的真空热压炉
- 915MHz MPCVD金刚石设备 微波等离子体化学气相沉积系统反应器
- 1200℃ 分体管式炉 石英管实验室管式炉
- 小型真空热处理及钨丝烧结炉



















