简短的回答是,没有一份单一的文件被称为铝热处理的“标准”。相反,行业使用一种标准化的编码系统,称为回火代号,来定义铝合金所经历的精确热处理和机械加工顺序。这个由美国铝业协会管理的系统使用一个字母后跟一个或多个数字(例如,6061-T6)来传达材料的最终机械性能。
理解铝回火代号系统是指定热处理的关键。这个代码不仅仅是命名一个过程;它描述了材料的整个热机械历史,从而也描述了其最终的强度、硬度和延展性。
基础:回火代号系统
回火代号是附加在合金编号后的后缀,例如6061-T6中的“T6”。这个简单的代码是工程师、冶金学家和机械师的通用语言。
基本代号
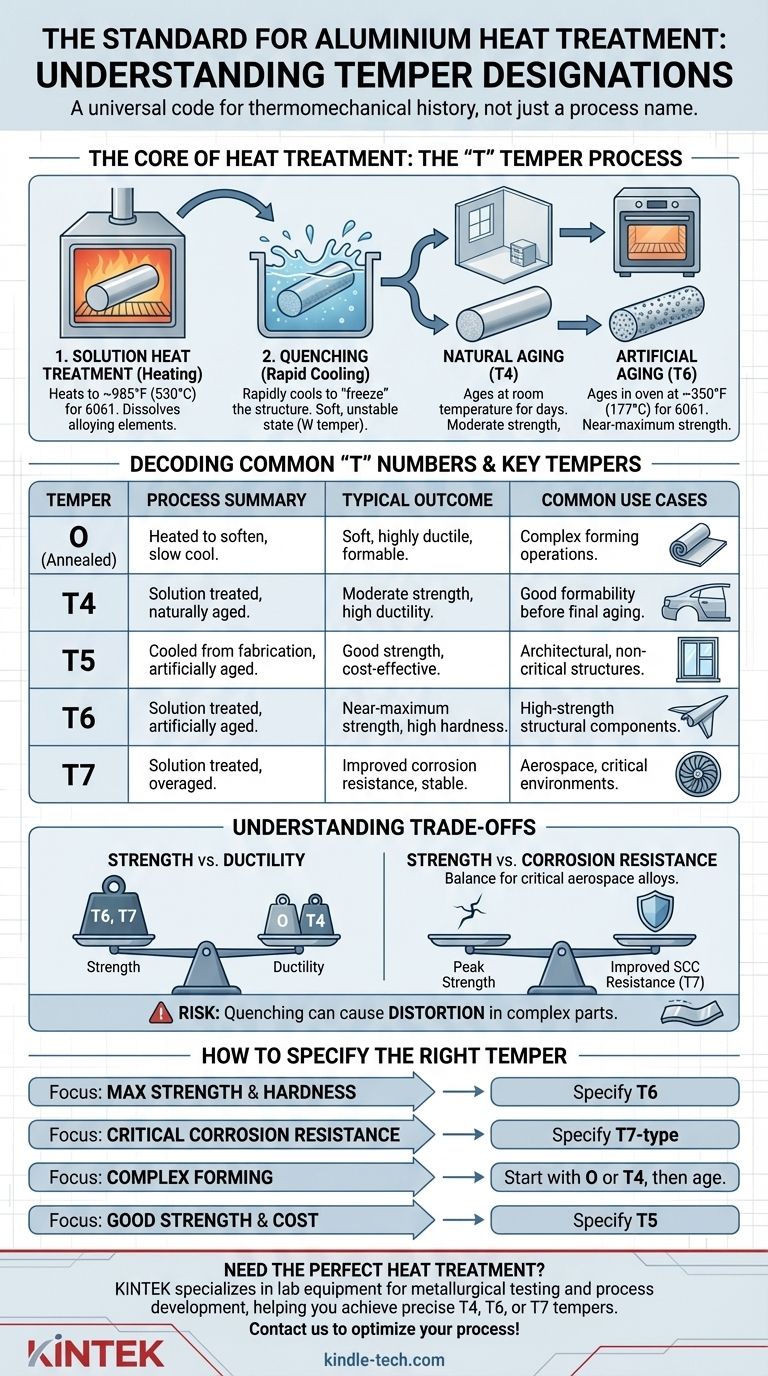
回火代号主要有五大类,每类由一个字母表示。其中只有“T”系列总是涉及热处理以产生硬化。
- F - 制造状态:这适用于对热处理或应变硬化条件没有特殊控制的产品。没有保证的机械性能。
- O - 退火状态:这是最软、延展性最好的回火状态。通过加热合金使其晶体结构重新形成,从而消除应力并最大化可加工性。
- H - 应变硬化状态:这仅适用于不可热处理合金(如3xxx或5xxx系列)。通过在冷态下对金属进行物理加工(例如轧制或拉拔)来增加强度。
- W - 固溶热处理状态:这是一种罕见且不稳定的回火状态。它代表固溶热处理和淬火后的即时状态,在任何时效发生之前。它通常仅用于内部过程控制。

解读“T”代号:热处理的核心
“T”回火状态是大多数人提到热处理铝时所指的。它适用于可热处理合金(如2xxx、6xxx和7xxx系列),表示材料通过特定的热处理过程得到了强化。
“T”回火的三步过程
获得稳定的“T”回火状态涉及一个精确的三阶段过程,称为沉淀硬化。
- 固溶热处理(加热):将铝加热到特定的高温(例如,6061合金约为985°F / 530°C)并保持。这会将主要的合金元素(如镁和硅)溶解成固溶体,就像糖溶解在热水中一样。
- 淬火(快速冷却):然后将材料快速冷却,通常在水中进行。这会将合金元素“冻结”在原位,形成过饱和固溶体。此时材料处于柔软、不稳定的状态(“W”回火状态)。
- 时效(沉淀硬化):将材料保持一段时间,可以在室温下进行,也可以在低温炉中进行。在此阶段,溶解的合金元素会以极其细小、分散的颗粒形式从溶液中沉淀出来,这些颗粒会阻碍位错运动,从而显著提高合金的强度和硬度。
自然时效与人工时效
最终性能取决于时效步骤的执行方式。
- 自然时效(T4):淬火后,零件在室温下放置数天进行时效。这会产生中等强度和高延展性的回火状态。
- 人工时效(T6):淬火后,零件在低温炉中(例如,6061合金约为350°F / 177°C)放置数小时。这会加速并控制沉淀,从而获得接近最大强度和硬度。
解读常见的“T”数字
“T”后面的数字提供了关于具体过程的更多细节。
- T4:固溶热处理后,自然时效至基本稳定状态。
- T5:从高温制造过程(如挤压)冷却后,再进行人工时效。这是一种成本较低的选择,可获得良好的强度,但不如T6强。
- T6:固溶热处理后,再进行人工时效。这是许多合金最常见的高强度回火状态。
- T7:固溶热处理后,再进行过时效(人工时效超过峰值强度)。这样做是为了提高尺寸稳定性和抗应力腐蚀开裂性。
理解权衡
选择回火代号是一项工程决策,涉及平衡相互竞争的性能。这绝不是简单地选择“最强”的选项。
强度与延展性
主要的权衡在于强度和延展性之间。O-回火状态(退火)的零件柔软且易于成形,但强度低。T6-回火状态的零件非常坚固但脆性大,不易成形。
强度与耐腐蚀性
对于某些合金,特别是航空航天中使用的7xxx系列,峰值强度伴随着更高的应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)敏感性。T7型回火状态有意牺牲一些强度,以显著提高SCC抵抗力,使其成为关键部件更安全的选择。
变形风险
淬火过程中的快速冷却是一种热冲击,会引起显著的内应力。这通常会导致薄壁或复杂零件变形。这种变形可能需要通过矫直或随后的应力消除操作来纠正。
如何指定正确的回火状态
您选择的回火状态必须由零件的功能、制造过程和使用环境决定。
- 如果您的主要关注点是最大强度和硬度:指定T6回火状态,因为这能为大多数常见合金提供最高的实用强度。
- 如果您的主要关注点是在关键环境中的耐腐蚀性:指定T7型回火状态(例如,T73、T76),以获得稳定性和抗应力腐蚀开裂性,同时接受强度的轻微降低。
- 如果您的主要关注点是成形复杂形状:首先使用O-回火状态或T4-回火状态的材料,进行成形操作,然后进行最终时效处理。
- 如果您的主要关注点是良好强度和较低成本的平衡:对于建筑或非关键结构应用,T5回火状态通常足够,因为不需要T6的极限性能。
归根结底,掌握铝热处理就是要使用这种标准代号系统,精确地将材料的性能与应用需求相匹配。
总结表:
| 回火代号 | 关键工艺 | 典型结果 | 常见用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O (退火) | 加热软化 | 柔软,高延展性 | 复杂成形操作 |
| T4 | 固溶热处理,自然时效 | 中等强度,高延展性 | 最终时效前具有良好成形性 |
| T5 | 从制造冷却,人工时效 | 良好强度,成本效益高 | 建筑,非关键结构 |
| T6 | 固溶热处理,人工时效 | 接近最大强度,高硬度 | 高强度结构部件 |
| T7 | 固溶热处理,过时效 | 改善耐腐蚀性,稳定 | 航空航天,关键环境 |
需要为您的项目指定完美的铝热处理吗?
KINTEK 专注于冶金测试和工艺开发所需的实验室设备和耗材。我们的专家可以帮助您选择合适的炉具和工具,以实现精确的 T4、T6 或 T7 回火状态,确保您的铝部件满足精确的强度、延展性和耐腐蚀性要求。
立即联系我们的团队 讨论您的应用并优化您的热处理工艺!
图解指南