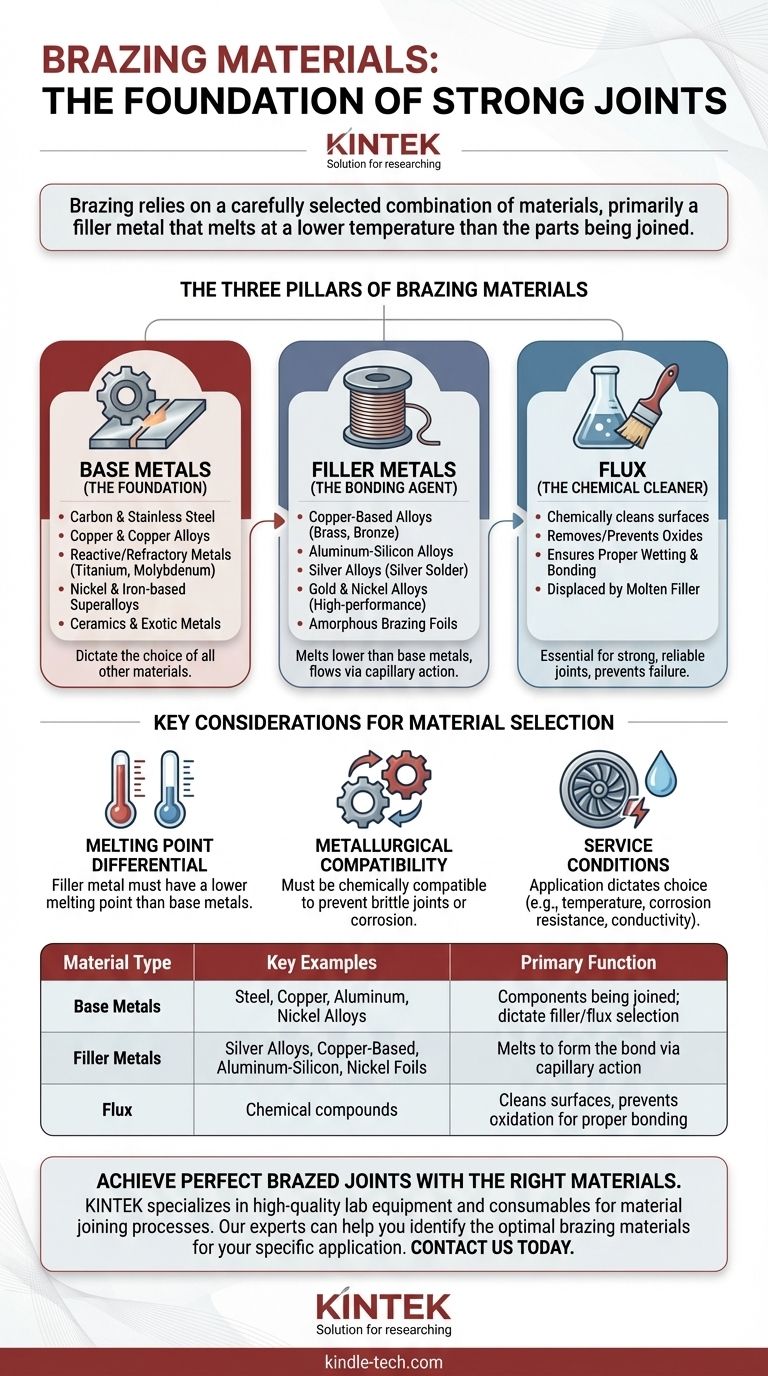
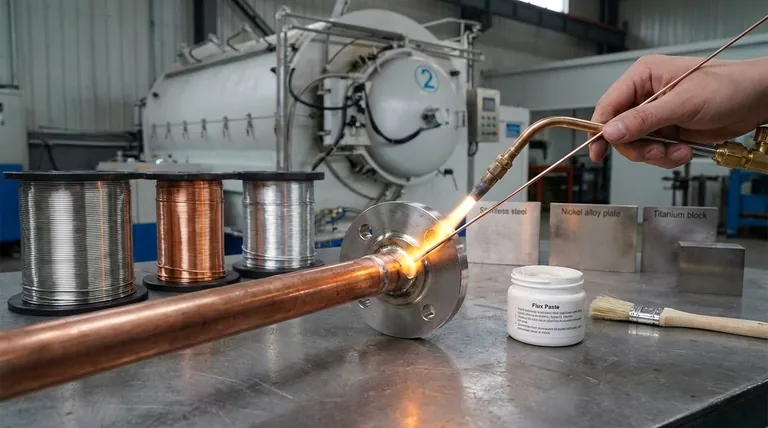
钎焊依赖于精心选择的材料组合,主要是填充金属,其熔点低于待连接部件的熔点。常见的填充金属包括铝硅合金、铜基合金(如黄铜和青铜)、银合金和镍基非晶态箔。它们与待连接的基材以及通常使用的化学焊剂协同作用,焊剂用于清洁表面以确保牢固的结合。
钎焊的核心原理是三种不同材料之间的相互作用:待连接的基材、熔点较低的填充金属以及用于准备表面以进行结合的焊剂。整个过程的成功取决于这三个组件的正确选择和兼容性。
钎焊材料的三大支柱
要全面了解钎焊中使用的材料,仅仅关注填充焊丝是不够的。该过程是一个系统,涉及部件本身、粘合剂和清洁剂。
基材:基础
基材是您试图连接在一起的组件。所有其他钎焊材料的选择都由这些金属的特性决定。
钎焊具有极强的通用性,可用于连接各种材料,从普通钢材到航空航天和国防等要求严苛的行业中使用的特种合金。
钎焊常用的基材示例包括:
- 碳钢、铸铁和不锈钢
- 铜和铜合金
- 钛、锆和钼等活性金属和难熔金属
- 镍基和铁基高温合金
- 陶瓷和铍等稀有金属
填充金属:粘合剂
填充金属是钎焊过程的核心。它被设计成在低于基材的温度下熔化,使其能够通过毛细作用被吸入紧密配合的接头中,然后在凝固后形成结合。
填充金属的成分决定了最终接头的强度、导电性和耐腐蚀性。
常见的填充金属系列:
- 铜基合金:广泛用于连接钢、铸铁和铜合金。这些填充剂,包括铜锌(黄铜)和铜锡(青铜),提供优异的导热和导电性。
- 铝硅合金:钎焊铝部件的标准选择,常用于汽车和HVAC应用。
- 银合金:常被称为“银焊料”,这些填充剂提供高强度和延展性,用于连接各种金属。
- 金和镍合金:用于需要极端耐腐蚀性、高温强度或特定冶金兼容性的高性能应用,例如航空航天或医疗设备。
- 非晶态钎焊箔:由镍、铁、硼和硅等元素制成的现代材料。这些箔提供精确、均匀的接头,在先进工程领域很常见。
焊剂:化学清洁剂
焊剂是许多钎焊操作中无名英雄。它的作用是通过在加热过程中去除并防止表面氧化物的形成来化学清洁基材和填充金属。
如果没有焊剂,这些氧化物将阻止填充金属润湿并与基材结合,导致接头薄弱或失效。焊剂在填充金属之前熔化,准备好表面,然后当熔融填充剂流入接头时被其取代。

材料选择的关键考虑因素
选择正确的材料组合并非随意;这是一个基于冶金学和最终组件预期应用的技术决策。
熔点差
钎焊最基本的规则是填充金属的熔点必须低于基材的熔点。这确保了被连接的组件在过程中不会熔化或变形。
冶金兼容性
填充金属必须与基材在化学和冶金上兼容。不兼容的组合可能导致脆性接头、腐蚀或其他形式的过早失效。
使用条件
最终应用决定了材料的选择。拖拉机的液压接头所需的性能与喷气发动机的涡轮叶片不同。工作温度、暴露于腐蚀性元素以及所需的导电性等因素必须指导填充金属的选择。
为您的应用选择材料
您的材料选择应由您正在连接的基材和最终组件的性能要求驱动。
- 如果您的主要重点是钢或铜的一般制造:铜基填充剂提供了一种经济高效且可靠的解决方案,具有良好的强度和导电性。
- 如果您的主要重点是连接铝部件:铝硅填充金属,搭配适当的焊剂,是标准且正确的选择。
- 如果您的主要重点是高性能或专业应用:镍、银或金基合金提供航空航天、国防或医疗组件所需的卓越强度、耐温性和耐腐蚀性。
了解基材、填充金属和焊剂的不同作用是创建坚固、可靠钎焊接头的关键。
总结表:
| 材料类型 | 主要示例 | 主要功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 基材 | 钢、铜、铝、镍合金 | 待连接的组件;决定填充剂/焊剂的选择 |
| 填充金属 | 银合金、铜基、铝硅、镍箔 | 熔化并通过毛细作用形成结合 |
| 焊剂 | 化学化合物(各种配方) | 清洁表面,防止氧化以实现良好结合 |
使用正确的材料实现完美的钎焊接头。选择基材、填充合金和焊剂的正确组合对于接头强度和性能至关重要。KINTEK 专注于为材料连接过程提供高质量的实验室设备和耗材。我们的专家可以帮助您确定特定应用的最佳钎焊材料,无论您是使用普通钢材还是先进合金。立即联系我们,讨论您的项目需求,确保可靠、高强度的结合。#联系表
图解指南